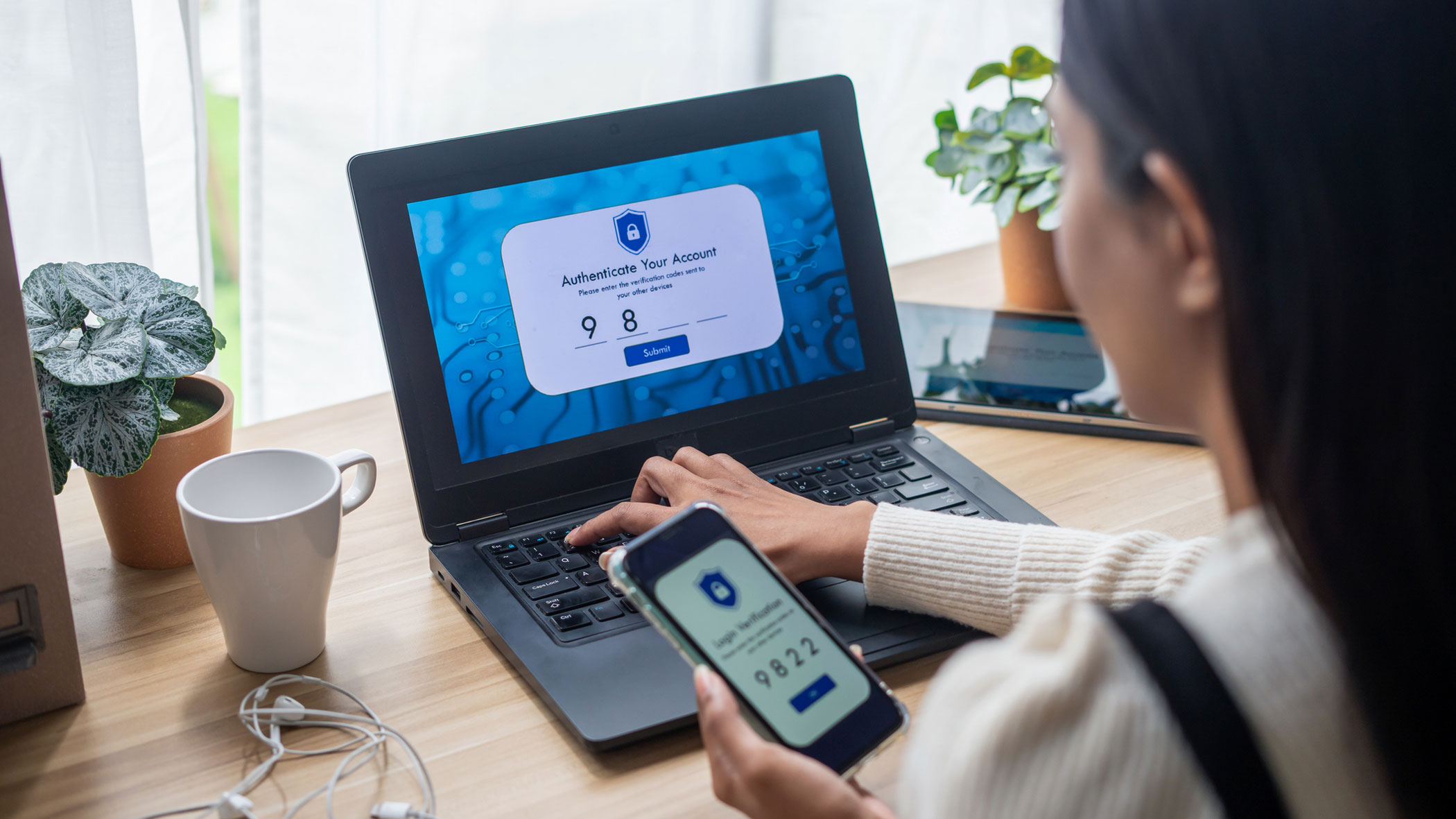
Scammers have been around forever, but modern technology has weaponized them in new and dangerous ways. In particular, spoofing has become more sophisticated and difficult to spot. Read on to learn what it is, how it works, and red flags that can alert you to a possible spoofing scam.
What is spoofing?
Spoofing is the act of disguising a communication from an unknown source to appear as if it’s being sent from a trusted source. The ultimate goal of spoofing is to get people to share their sensitive information and/or their money or credit card details with the scammer. For example, a spoofer may pretend to represent a victim’s credit card company and lead them into sharing their full credit card details to make unauthorized purchases, or they may impersonate their bank or credit union to get them to share their online banking username and password to illegally transfer money to their own account.
Types of spoofing
Cybercriminals use a variety of communication methods to pull off their spoofing. Here are the more common forms:
Text message spoofing
In this scam, a victim receives a text message appearing to come from a trusted source, such as the victim’s financial institution, place of work, or doctor’s office. The text will ask the victim to share personal information. Text message spoofing is so sneaky and dangerous because many victims mistakenly believe the sender of the text message is who they claim to be.
Read more about text message scams in our blog posts:
Email spoofing
In email spoofing, an attacker sends an email message appearing to be from a known or trusted source. The emails typically include links to harmful websites, that criminals use to steal your sensitive data, or attachments that will infect the victim’s device with malware. Malware is software designed to gain unauthorized access to someone’s device, such as a smart phone or computer, to steal personal information.
Caller ID spoofing
These attackers call their target, appearing to be from a known number. The scammer will often pose as the victim’s credit union or bank. The victim, believing they are speaking with a representative of their financial institution, will disclose their account information and even passwords, which can lead to the scammer emptying their accounts and/or stealing their identity. Sometimes, the scammer will provide the victim with a phone number to call, which will allegedly connect them with their bank or credit union. This number only connects the victim to that scammer.
Important: MSGCU will NEVER ask you to reveal your Online or Mobile Banking password or login verification code. If someone calls requesting this information, hang up, it’s a scam. Then call MSGCU at (866) 674-2848 or (586) 263-8800.
Website spoofing
In website spoofing, a scammer will create a fake site that looks just like a reputable website that the victim often visits. Attackers will lure victims to this site for the purpose of stealing their login credentials and personal information. Verify a website is secure by checking the website address. If the website starts with “https” and displays a lock icon next to the URL (the website address), it is secure. Never input your personal information into unsecure websites, those that start with just “http.”
If you’re ever unsure about a website being real or fake, try searching for scams related to the website or avoid it all together.
Deepfakes and spoofing
Deepfakes is a relatively new and dangerous tool for spoofers. A deepfake is a fake image, video, or audio clip that has been edited to appear authentic. For instance, a scammer may create a deepfake video using an image and audio recording of a celebrity and make it appear as if they are telling you to open a link or support a specific cause.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, voice cloning, another form of deepfakes, is also on the rise. A scammer will contact an individual and pretend to be their boss or a loved one. The scammer uses AI technology to sound like someone the victim knows to get bank account, or credit/debit card information, or other personal information. If you suspect a scammer called you pretending to be someone you know with voice cloning, hang up and call or contact that person directly to confirm if it was them that reached out to you.
Scammers use deepfakes to trap victims and appear as if they represent or are a trusted source.
Red flags
Look out for these red flags to avoid a possible spoofing attack:
- You’re asked to share your login credentials or a one-time login verification pin. No legitimate financial institution will ask you for your online or mobile banking password.
- Websites with a URL that is very similar to the URL of a reputable site. For example, a website claims to be for your favorite store, but it is spelled incorrectly or has extra characters in the URL.
- Websites with typos, unusual syntax and grammar, and spelling errors.
- An alleged rep of your bank or credit union asks you to call a number that is not associated with your financial institution. Only contact MSGCU at (866) 674-2848 or (586) 263-8800.
- You receive a message with an unusual call-to-action, and the scammer uses familiar corporate branding like colors and logos to make it appear real.
- You receive an unexpected call from your boss, a friend, or family member saying they are facing an emergency and urgently need money or bank account information.
Protect yourself
Spoofing is a lurking danger for all consumers. Arming yourself with the right knowledge can help you avoid falling victim to these scams. Here’s how to protect yourself from a spoofing attack:
- Turn on your email’s spam filter and be sure to mark incoming emails that look suspicious as spam.
- Use two-factor authentication and/or biometric logins (your face or fingerprint) whenever possible.
- Use strong, unique passwords across all of your accounts. Read more about password tips in this blog.
- Make sure your device's security system is up to date. Check your device’s settings for updates. Read more here.
- Never click on links or open attachments that you are not expecting, including those sent from an unverified source.
- Never share personal information online or over the phone with an unknown contact.
- If you’re allegedly contacted by your financial institution and asked to provide your login credentials or account details, do NOT respond. Instead, delete the message or end the call and contact your bank or credit union directly to ask about any possible issues with your account. You can contact MSGCU at (866) 674-2848 or (586) 263-8800.
- Don’t take all phone calls at face value, even with caller ID. Criminals have ways to easily change the phone number to make it look like a legitimate one.
- Identify deepfakes by looking for differences in facial features. Zoom into the image or video to verify if the words and lip movements are in sync. Look for changes from the person’s normal appearance such as lip color that looks unnatural, unrealistic facial hair, exaggeratedly wrinkled or smooth skin, or the absence/presence of moles or other distinguishable features.
- If you’re ever unsure of a communication that claims to be from MSGCU, contact our team at (866) 674-2848 or (586) 263-8800 or visit any branch office.
If you’ve been targeted
If you believe you’ve shared sensitive information with a scammer through a spoofing attack, there are steps you can take to mitigate the damage.
- Contact your financial institution right away to let them know about the attack so steps can be taken to secure your account.
- If your credit or debit card information was compromised, contact your financial institution to freeze your cards and get new card numbers. You can also quickly deactivate your MSGCU cards through Online and Mobile Banking. Navigate to “Card Controls” from the left main menu to do so.
- If you believe your identity has been stolen, check out identitytheft.gov to learn what your next step should be.
- Change the passwords on all your accounts to protect them from further attacks. Use password best practices.
Spoofing has gotten a lot more dangerous and harder to spot in recent years, but with proper awareness and protective measures, you can avoid getting scammed.
Category: Security
« Return to "Blog"